template<class type_t,
xtd::size rank_, class allocator_t>
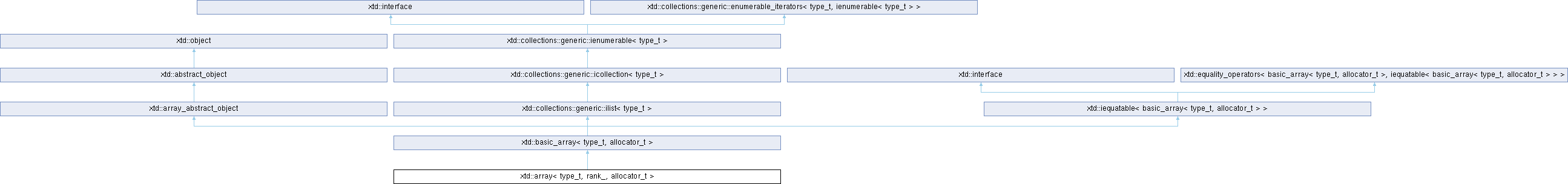
class xtd::array< type_t, rank_, allocator_t >
Provides methods for creating, manipulating, searching, and sorting arrays, thereby serving as the base class for all arrays.
- Definition
template<class type_t, xtd::size rank_, class allocator_t>
Base object that represent array.
Definition basic_array.hpp:27
- Header
-
- Namespace
- xtd
- Library
- xtd.core
- Examples
- The following code example demonstrates different methods to create an array.
- Examples
- The following code example creates and initializes an Array and displays its properties and its elements.
#include <xtd/xtd>
auto print_values(const array<int>& my_arr) {
for (auto i : my_arr)
}
for (auto o : my_arr)
}
auto main() -> int {
auto my_int_array = array<int> {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
auto my_obj_array = array<any_object> {26, 27, 28, 29, 30};
console::write_line("Initially,");
console::write("integer array:");
print_values(my_int_array);
console::write("Object array: ");
print_values(my_obj_array);
array<>::copy(my_int_array, my_obj_array, 2);
console::write_line("\nAfter copying the first two elements of the integer array to the Object array,");
console::write("integer array:");
print_values(my_int_array);
console::write("Object array: ");
print_values(my_obj_array);
xtd::array<>::copy(my_obj_array, my_obj_array.get_upper_bound(0) - 1, my_int_array, my_int_array.get_upper_bound(0) - 1, 2);
console::write_line("\nAfter copying the last two elements of the Object array to the integer array,");
console::write("integer array:");
print_values(my_int_array);
console::write("Object array: ");
print_values(my_obj_array);
}
static void copy(const array< source_type_t, source_rank, source_allocator_t > &source_array, const array< destination_type_t, destination_rank, destination_allocator_t > &destination_array)
Copies a range of elements from an xtd::array starting at the first element and pastes them into anot...
Definition array_static.hpp:239
Provides methods for creating, manipulating, searching, and sorting arrays, thereby serving as the ba...
Definition array.hpp:64
static void write(arg_t &&value)
Writes the text representation of the specified value to the standard output stream.
Definition console.hpp:462
static void write_line()
Writes the current line terminator to the standard output stream using the specified format informati...
- Examples
- date_time_format_info.cpp, date_time_now.cpp, form_paint.cpp, graphics.cpp, ienumerable.cpp, and ilist.cpp.
|
| | array ()=default |
| | Initializes a new instance of the array class that is empty.
|
| | array (const array &array) |
| | Copy constructor with specified array.
|
| | array (array &&array) |
| | Move constructor with specified array.
|
| | array (const array< xtd::size, 1 > &lengths) |
| | Initializes a new instance of the array class with lengths for each rank specified.
|
| | array (const array< xtd::size, 1 > &lengths, const type_t &value) |
| | Initializes a new instance of the array class with lengths for each rank specified.
|
| | array (const xtd::collections::generic::ienumerable< type_t > &enumerable) |
| | Initializes a new instance of the array and copy array array specified.
|
| | array (const xtd::collections::generic::ilist< type_t > &list) |
| | Initializes a new instance of the array and copy array array specified.
|
| template<class input_iterator_t> |
| | array (input_iterator_t first, input_iterator_t last) |
| | Constructs the container with the contents of the range [first, last).
|
| | array (std::initializer_list< type_t > items) |
| | Constructs the container with the contents of the specified initializer list.
|
|
| using | value_type |
| | Represents the array value type.
|
| using | allocator_type |
| | Represents the array allocator type.
|
| using | base_type |
| | Represents the array base type.
|
| using | size_type |
| | Represents the array size type (usually xtd::size).
|
| using | difference_type |
| | Represents the array difference type (usually xtd::ptrdiff).
|
| using | reference |
| | Represents the reference of array value type.
|
| using | const_reference |
| | Represents the const reference of array value type.
|
| using | pointer |
| | Represents the pointer of array value type.
|
| using | const_pointer |
| | Represents the const pointer of array value type.
|
| using | iterator |
| | Represents the iterator of array value type.
|
| using | const_iterator |
| | Represents the const iterator of array value type.
|
| using | reverse_iterator |
| | Represents the reverse iterator of array value type.
|
| using | const_reverse_iterator |
| | Represents the const reverse iterator of array value type.
|
| size_type | count () const noexcept override |
| | Gets the number of elements contained in the xtd::array <type_t>.
|
| virtual pointer | data () noexcept |
| | Returns pointer to the underlying array serving as element storage.
|
| bool | is_fixed_size () const noexcept override |
| | Gets a value indicating whether the xtd::collections::generic::ilist <type_t> has a fixed size.
|
| bool | is_read_only () const noexcept override |
| | Gets a value indicating whether the xtd::collections::generic::icollection <type_t> is read-only.
|
| bool | is_synchronized () const noexcept override |
| | Gets a value indicating whether access to the xtd::collections::generic::icollection <type_t> is synchronized (thread safe).
|
| virtual const base_type & | items () const noexcept |
| | Returns the underlying base type items.
|
| virtual size_type | length () const noexcept |
| | Gets a size that represents the total number of elements in all the dimensions of the array.
|
| virtual xtd::int64 | long_length () |
| | Gets a 64-bit integer that represents the total number of elements in all the dimensions of the array.
|
| virtual size_type | max_length () const noexcept |
| | Returns the maximum number of elements the container is able to hold due to system or library implementation limitations, i.e. std::distance(xtd::array::begin(), xtd::array::end()) for the largest container.
|
| const xtd::object & | sync_root () const noexcept override |
| | Gets an object that can be used to synchronize access to the the xtd::collections::generic::icollection <type_t>.
|
| bool | contains (const type_t &value) const noexcept override |
| | Determines whether an element is in the array.
|
| void | copy_to (xtd::array< type_t > &array) const |
| | Copies the entire xtd::array <type_t> to a compatible one-dimensional array.
|
| bool | equals (const object &obj) const noexcept override |
| | Determines whether the specified object is equal to the current object.
|
| virtual void | fill (const value_type &value) noexcept |
| | Assigns the value to all elements in the container.
|
|
xtd::collections::generic::enumerator< value_type > | get_enumerator () const noexcept override |
| constexpr size_type | get_length (size_type dimension) const |
| | Gets the total number of elements in all the dimensions of the array.
|
| xtd::array< size_type, 1 > | get_lengths () const |
| | Gets an array of the number of elements of all the dimensions of the array.
|
| constexpr xtd::int64 | get_long_length (size_type dimension) const |
| | Gets a 64-bit integer that represents the total number of elements in all the dimensions of the array.
|
| constexpr size_type | get_lower_bound (size_type dimension) const |
| | Gets the lower bound of the specified dimension in the array.
|
| constexpr size_type | get_upper_bound (size_type dimension) const |
| | Gets the upper bound of the specified dimension in the array.
|
| const value_type & | get_value (const xtd::array< size_type > &indexes) const |
| | Gets the value at the specified position in the multidimensional array. The indexes are specified as 32-bit integers array.
|
| size_type | index_of (const type_t &value) const noexcept override |
| | Determines the index of a specific item in the xtd::array <type_t>.
|
| void | set_value (const type_t &value, const xtd::array< size_type > &indexes) |
| | Resizes the container to contain count elements, does nothing if count == length().
@param new_size The new size of the container.
@exception xtd::argument_out_of_range_exception xtd::collections::generic::list::capacity is set to a value that is less than xtd::collections::generic::list::count.
@remarks If the current size is greater than count, the container is reduced to its first count elements.
@remarks If the current size is less than count`, additional default-inserted elements are appended. */ void resize(size_type new_size) {resize(new_size, value_type {});}.
|
| basic_array< type_t > & | sort () |
| | Sorts the elements in the entire xtd::collections::generic::list <type_t> using the default comparer.
|
| xtd::string | to_string () const noexcept override |
| | Returns a xtd::string that represents the current object.
|
| basic_array & | operator= (const basic_array &other) |
| | Copy assignment operator. Replaces the contents with a copy of the contents of other.
|
| const_reference | operator[] (size_type index) const override |
| | Returns a reference to the element at specified location index.
|
| | operator const base_type & () const noexcept |
| | Returns a reference to the underlying base type.
|
| | operator base_type & () noexcept |
| | Returns a reference to the underlying base type.
|
| type_t & | operator() (const xtd::array< size_type > &indexes) |
| | Gets the value at the specified position in the multidimensional array. The indexes are specified as a 32-bit integer array.
|
| | object ()=default |
| | Create a new instance of the ultimate base class object.
|
| virtual xtd::size | get_hash_code () const noexcept |
| | Serves as a hash function for a particular type.
|
| virtual type_object | get_type () const noexcept |
| | Gets the type of the current instance.
|
| template<class object_t> |
| xtd::unique_ptr_object< object_t > | memberwise_clone () const |
| | Creates a shallow copy of the current object.
|
| virtual bool | equals (const type_t &) const noexcept=0 |
| | Indicates whether the current object is equal to another object of the same type.
|
| template<class object_a_t, class object_b_t> |
| static bool | equals (const object_a_t &object_a, const object_b_t &object_b) noexcept |
| | Determines whether the specified object instances are considered equal.
|
| template<class object_a_t, class object_b_t> |
| static bool | reference_equals (const object_a_t &object_a, const object_b_t &object_b) noexcept |
| | Determines whether the specified object instances are the same instance.
|
| | abstract_object ()=default |
| | Initializes a new instance of the xtd::abstract_object class.
|