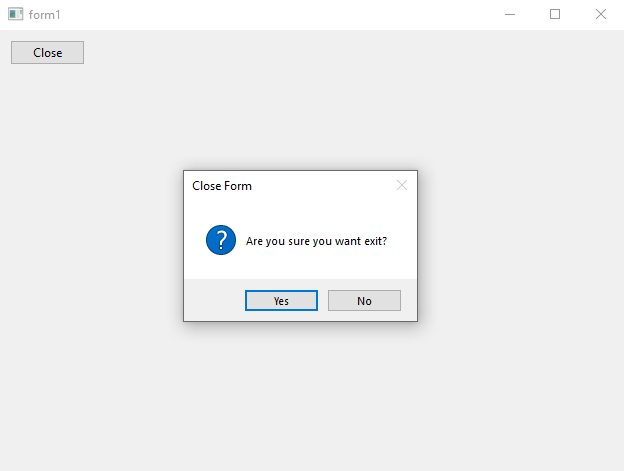
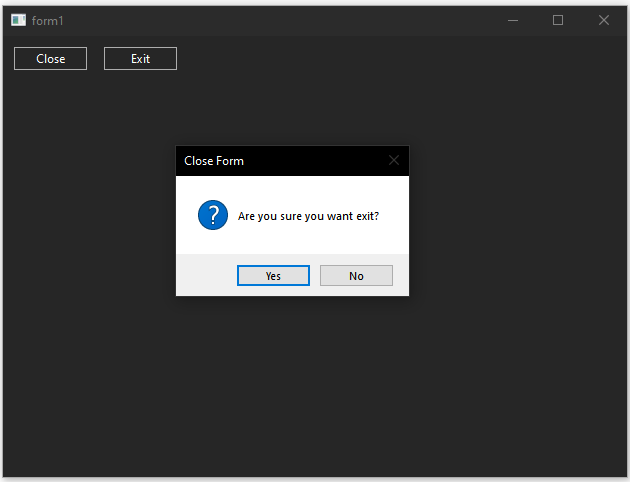
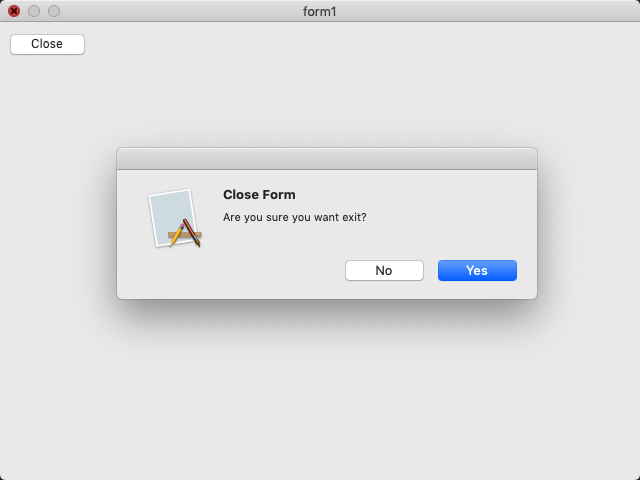
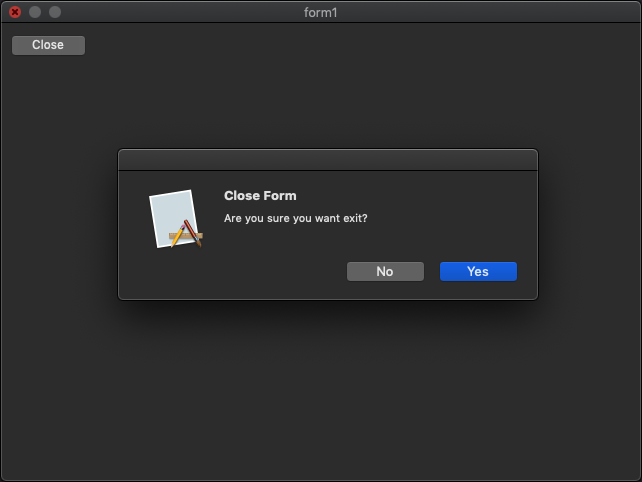
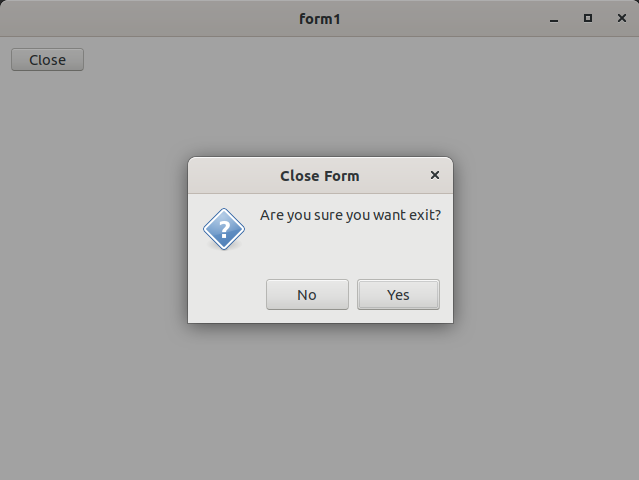
The following code example demonstrate the use of form control.
#include <xtd/xtd>
using namespace std;
class form1 :
public form {
public:
form1() {
text("form1");
location({300, 200});
button_close.parent(*this);
button_close.text("Close");
button_close.auto_size(true);
button_close.location({10, 10});
button_exit.parent(*this);
button_exit.text("Exit");
button_exit.auto_size(true);
button_exit.location({100, 10});
button_exit.click += overload_<>(&application::exit);
button_exit_thread.parent(*this);
button_exit_thread.text("Exit thread");
button_exit_thread.auto_size(true);
button_exit_thread.location({190, 10});
button_exit_thread.click += &application::exit_thread;
}
protected:
e.cancel(message_box::show(*this, "Are you sure you want exit?", "Close Form", message_box_buttons::yes_no, message_box_icon::question) == dialog_result::no);
};
private:
};
int main() {
application::run(form1());
}
generic_event_handler<> event_handler
Represents the method that will handle an event that has no event data.
Definition event_handler.h:33
size_t size
Represents a size of any object in bytes.
Definition types.h:171
The xtd namespace contains all fundamental classes to access Hardware, Os, System,...
Definition system_report.h:17