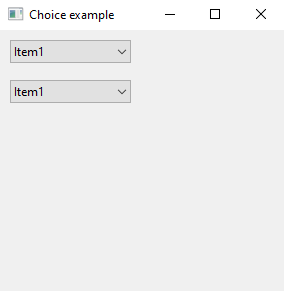
The following code example demonstrate the use of choice control.
#include <xtd/xtd>
namespace examples {
class form1 : public form {
public:
form1() {
text("Choice example");
choice1.parent(*this);
choice1.location({10, 10});
choice1.items().push_back_range({"Item1", "Item2", "Item3", "Item4", "Item5", "Item6", "Item7", "Item8", "Item9", "Item10"});
choice1.selected_index(0);
choice1.selected_index_changed +=
event_handler(*
this, &form1::on_choice_click);
choice2.parent(*this);
choice2.location({10, 50});
choice2.items().push_back_range({"Item1", "Item2", "Item3", "Item4", "Item5", "Item6", "Item7", "Item8", "Item9", "Item10"});
choice2.selected_index(0);
choice2.selected_index_changed +=
event_handler(*
this, &form1::on_choice_click);
}
private:
choice1.selected_index(as<choice&>(sender).selected_index());
choice2.selected_index(as<choice&>(sender).selected_index());
}
choice choice1;
choice choice2;
};
}
int main() {
application::run(examples::form1());
}
Represents the base class for classes that contain event data, and provides a value to use for events...
Definition: event_args.h:18
generic_event_handler<> event_handler
Represents the method that will handle an event that has no event data.
Definition: event_handler.h:33
The xtd::drawing namespace provides access to GDI+ basic graphics functionality. More advanced functi...
Definition: bitmap.h:11
The xtd namespace contains all fundamental classes to access Hardware, Os, System,...
Definition: system_report.h:17