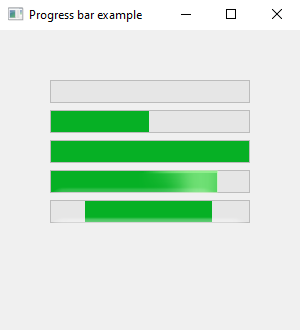
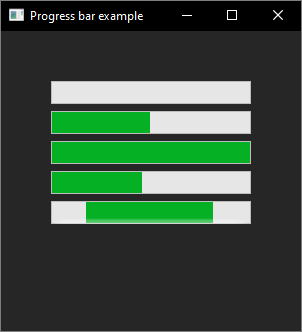
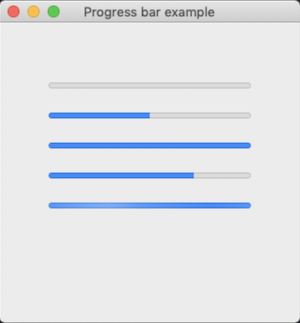
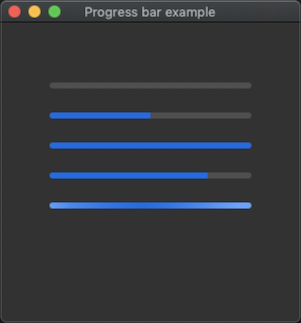
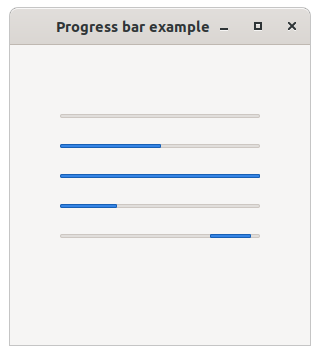
The following code example demonstrate the use of progress_bar control.
#include <xtd/xtd>
using namespace std::literals;
namespace examples {
class form1 :
public form {
public:
form1() {
text("Progress bar example");
client_size({300, 300});
progress_bar1.parent(*this);
progress_bar1.location({50, 50});
progress_bar1.width(200);
progress_bar2.parent(*this);
progress_bar2.location({50, 80});
progress_bar2.value(50);
progress_bar2.width(200);
progress_bar3.parent(*this);
progress_bar3.location({50, 110});
progress_bar3.maximum(300);
progress_bar3.increment(300);
progress_bar3.width(200);
progress_bar4.parent(*this);
progress_bar4.location({50, 140});
progress_bar4.step(1);
progress_bar4.width(200);
progress_bar5.parent(*this);
progress_bar5.location({50, 170});
progress_bar5.maximum(200);
progress_bar5.minimum(100);
progress_bar5.style(progress_bar_style::marquee);
progress_bar5.width(200);
timer1.interval(50ms);
timer1.tick += [&] {
progress_bar4.value(progress_bar4.value() < progress_bar4.maximum() ? progress_bar4.value() + 1 : progress_bar4.minimum());
};
timer1.enabled(true);
}
private:
};
}
int main() {
application::run(examples::form1());
}